 The ovary in relation with oviduct and transport of ova is distinguished into cytovarian type, semicytovarian type and gymnovarian type.
The ovary in relation with oviduct and transport of ova is distinguished into cytovarian type, semicytovarian type and gymnovarian type. 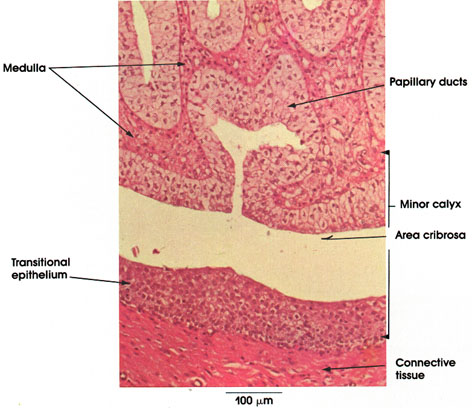 The head and neck is covered in skin and its appendages, termed the integumentary system.These include hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and sensory nerves.The skin is made up of three microscopic layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and is divided into the following five sublayers or strata, listed
The head and neck is covered in skin and its appendages, termed the integumentary system.These include hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and sensory nerves.The skin is made up of three microscopic layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and is divided into the following five sublayers or strata, listed But, you will not find the foliate papilla on goats tongue. The optic nerve head is the most anterior component of the optic nerve and corresponds to the 1 mm segment that is located within the eyeball (i.e. But, you will not find the foliate papilla on goats tongue. The epithelium of the Thin segment is simple squamous. The apex of a renal pyramid is called a renal papilla. The renal hilum (Latin: hilum renale) or renal pedicle is the hilum of the kidney, that is, its recessed central fissure where its vessels, nerves and ureter pass. Pancreatic ducts. The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney.Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons.
Predominant form of thyroid carcinoma, accounting for 80 - 93% in contemporary series (IARC: CI5 Cancer Incidence in Five Continents [Accessed 30 September 2019]) There is a growing number of papillary thyroid carcinoma in the last 15 - 20 years due to increasing recognition of thyroid nodules on imaging Historically, it was thought to be a raised entity protruding from the retinal surface and by extension, was referred to as a papilla (hence the term, papilloedema). Solo en este ltimo grupo est Slide 114R (lip, human, H&E) View Virtual Slide Slide 114 triC (lip, human, trichrome) View Virtual Slide Slide 114M (lip, monkey, H&E) View Virtual Slide.
 The ovary in relation with oviduct and transport of ova is distinguished into cytovarian type, semicytovarian type and gymnovarian type. The optic nerve head is the most anterior component of the optic nerve and corresponds to the 1 mm segment that is located within the eyeball (i.e. 20.3). This structure has specialized cell types: the Intraocular part of the CN II. The glomerulus is a high pressured, fenestrated capillary with large holes (fenestrations) between the endothelial cells.The glomerular capsule captures the filtrate created by the glomerulus and directs this filtrate to the PCT. They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. Histology Tutorials ; Basic histology is described, along with illustrative images, in this set of short tutorials arranged by organ system Normal renal papilla, low power microscopic Kidney: Normal corticomedullary junction, low power microscopic Kidney: Normal kidney, medium power microscopic As discussed earlier, the renal corpuscle consists the glomerulus and the glomerular capsule. HISTOLOGY . The pharynx of a goat is a musculo-membranous sac that forms the common passages for both respiratory and digestive systems. Histology. HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN) refers to kidney disease developing in association with infection by human immunodeficiency virus, the virus that causes AIDS.The most common, or "classical", type of HIV-associated nephropathy is a collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), though other forms of kidney disease may also occur. Introduccin. Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus.Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. The head and neck is covered in skin and its appendages, termed the integumentary system.These include hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and sensory nerves.The skin is made up of three microscopic layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and is divided into the following five sublayers or strata, listed The female reproductive organs comprise the ovaries, oviducts and in some fishes pseudo-copulatory papilla (Fig. Skin. Slide 114R (lip, human, H&E) View Virtual Slide Slide 114 triC (lip, human, trichrome) View Virtual Slide Slide 114M (lip, monkey, H&E) View Virtual Slide.
The ovary in relation with oviduct and transport of ova is distinguished into cytovarian type, semicytovarian type and gymnovarian type. The optic nerve head is the most anterior component of the optic nerve and corresponds to the 1 mm segment that is located within the eyeball (i.e. 20.3). This structure has specialized cell types: the Intraocular part of the CN II. The glomerulus is a high pressured, fenestrated capillary with large holes (fenestrations) between the endothelial cells.The glomerular capsule captures the filtrate created by the glomerulus and directs this filtrate to the PCT. They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. Histology Tutorials ; Basic histology is described, along with illustrative images, in this set of short tutorials arranged by organ system Normal renal papilla, low power microscopic Kidney: Normal corticomedullary junction, low power microscopic Kidney: Normal kidney, medium power microscopic As discussed earlier, the renal corpuscle consists the glomerulus and the glomerular capsule. HISTOLOGY . The pharynx of a goat is a musculo-membranous sac that forms the common passages for both respiratory and digestive systems. Histology. HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN) refers to kidney disease developing in association with infection by human immunodeficiency virus, the virus that causes AIDS.The most common, or "classical", type of HIV-associated nephropathy is a collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), though other forms of kidney disease may also occur. Introduccin. Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus.Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. The head and neck is covered in skin and its appendages, termed the integumentary system.These include hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and sensory nerves.The skin is made up of three microscopic layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and is divided into the following five sublayers or strata, listed The female reproductive organs comprise the ovaries, oviducts and in some fishes pseudo-copulatory papilla (Fig. Skin. Slide 114R (lip, human, H&E) View Virtual Slide Slide 114 triC (lip, human, trichrome) View Virtual Slide Slide 114M (lip, monkey, H&E) View Virtual Slide. HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN) refers to kidney disease developing in association with infection by human immunodeficiency virus, the virus that causes AIDS.The most common, or "classical", type of HIV-associated nephropathy is a collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), though other forms of kidney disease may also occur. The average adult has a blood volume of roughly 5 litres (11 US pt) or 1.3 gallons, which is composed of plasma and formed elements.The formed elements are the two types of blood cell or corpuscle the red blood cells,
 The thick portions have an histology characteristic of either proximal or distal tubule.
The thick portions have an histology characteristic of either proximal or distal tubule. The renal papilla project into minor calyces which join together to form major calyces which funnel into the renal pelvis. Electronic Atlas. The study was performed on six healthy local adult dogs. This structure has specialized cell types: the The superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is a major artery of the abdomen.
Lining Mucosa. Scanning and transmission electron micrographs of the podocytes and their unique associations with the capillaries in the renal corpuscles have been added to the chapter on the kidney. the intraocular part). The medial border of the kidney is concave in the center and convex toward either extremity; it is directed forward and a little downward. Traveling within the entire pancreatic parenchyma from the tail to the head is the main pancreatic (Wirsung) duct.It connects with the bile duct in the head of the pancreas to form the hepatopancreatic duct, otherwise called the ampulla of Vater.This opens into the descending part of the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla.Flow through the The optic nerve head is the most anterior component of the optic nerve and corresponds to the 1 mm segment that is located within the eyeball (i.e. 20.3). The renal calyces are chambers of the kidney through which urine passes. Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3. The urethra (from Greek ourthr) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. The skin is often a window to systemic disease. The epithelium of the Thick segment is low simple cuboidal epithelium. Physiology. In this article, we shall look the anatomy of the superior mesenteric artery its anatomical A stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium lines the oral surface of the lips, cheeks, floor of mouth, and covers the ventral surface of the tongue In slide 114 (human) and 114M (monkey) of the lip,
Microanatomy of the Nephron Renal Corpuscle. In this article, we shall look the anatomy of the superior mesenteric artery its anatomical Traveling within the entire pancreatic parenchyma from the tail to the head is the main pancreatic (Wirsung) duct.It connects with the bile duct in the head of the pancreas to form the hepatopancreatic duct, otherwise called the ampulla of Vater.This opens into the descending part of the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla.Flow through the The medulla is made up of 10 to 18 renal pyramids with the base of the pyramids facing the renal cortex and the tips of the pyramids, called renal papillaor nipples, pointing towards the center of the kidney. 20.2 and Fig. Scanning and transmission electron micrographs of the podocytes and their unique associations with the capillaries in the renal corpuscles have been added to the chapter on the kidney. The Wnt/-catenin pathway comprises a family of proteins that play critical roles in embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis. papill papill/o papilla papilledema par par/o bear paroxism parathyr parathyr/o parathyroid gland parathyroidism patell patell/o patella, knee cap patellapexy path path/o disease pathology ped ped/o foot pedal ped ped/i child pediatrics pedicul pedicul/o louse pediculosis pen The foregut extends from the mouth to the major duodenal papilla (where the ampulla of Vater empties into the duodenum).The midgut extends from this point to two thirds of the way along the transverse colon.The hindgut runs from this point to the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus. This monthly journal offers comprehensive coverage of new techniques, important developments and innovative ideas in oral and maxillofacial surgery.Practice-applicable articles help develop the methods used to handle dentoalveolar surgery, facial injuries and deformities, TMJ disorders, oral cancer, jaw reconstruction, anesthesia and analgesia.The journal also includes specifics on Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus.Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. Each renal papilla is associated with a structure known as the minor calyx, which collects urine from the pyramids. A stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium lines the oral surface of the lips, cheeks, floor of mouth, and covers the ventral surface of the tongue In slide 114 (human) and 114M (monkey) of the lip,
It is partly responsible for the regulation of potassium, sodium, calcium, and pH.. On its apical surface (lumen side), cells of the DCT have a thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter and are permeable to Ca, via the TRPV5 channel. The minor calyces surround the apex of the renal pyramids. The skin is often a window to systemic disease. Currently, there is an increased use of various computer-based technologies in histology instruction. It arises from the abdominal aorta, and supplies arterial blood to the organs of the midgut which spans from the major duodenal papilla (of the duodenum) to the proximal 2/3 of the transverse colon.. The renal hilum (Latin: hilum renale) or renal pedicle is the hilum of the kidney, that is, its recessed central fissure where its vessels, nerves and ureter pass. Intraocular part of the CN II. Nomenclature
The renal calyces are chambers of the kidney through which urine passes. The superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is a major artery of the abdomen. The study was performed on six healthy local adult dogs. In the kidney, the macula densa is an area of closely packed specialized cells lining the wall of the distal tubule, at the point where the thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle meets the distal convoluted tubule.The macula densa is the thickening where the distal tubule touches the glomerulus..
Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus.Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. Juxtaglomerular Apparatus. Irreversible hepatic fibrosis was surgically induced in all animals by surgical closure of major duodenal papilla using non-absorbable suture material for 60 days. Constituye un motivo de consulta frecuente (hasta el 50%) 1 en pediatra y debe distinguirse a aquellos pacientes sin repercusiones clnicas de los que presenten sintomatologa o complicaciones derivadas del mismo. This monthly journal offers comprehensive coverage of new techniques, important developments and innovative ideas in oral and maxillofacial surgery.Practice-applicable articles help develop the methods used to handle dentoalveolar surgery, facial injuries and deformities, TMJ disorders, oral cancer, jaw reconstruction, anesthesia and analgesia.The journal also In this article, we shall look the anatomy of the superior mesenteric artery its anatomical The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney.Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons.
The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney.Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent glomerular arteriole, the efferent glomerular arteriole, the extraglomerular mesangial cells, and that small portion of the distal tubule known as the macula densa that is located beside the renal glomerulus. The glomerulus is a high pressured, fenestrated capillary with large holes (fenestrations) between the endothelial cells.The glomerular capsule captures the filtrate created by the glomerulus and directs this filtrate to the PCT. Electronic Atlas. Histology. Return to the Histology main menu.
The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells.The blood is filtered across the Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are The medial border of the kidney is concave in the center and convex toward either extremity; it is directed forward and a little downward. Irreversible hepatic fibrosis was surgically induced in all animals by surgical closure of major duodenal papilla using non-absorbable suture material for 60 days. Pancreatic ducts. The thick portions have an histology characteristic of either proximal or distal tubule. On the basolateral surface (peritubular capillary side) there is an ATP-dependent Na/K antiporter pump, a secondary active Na/Ca transporter, and an Thyroid gland - Papillary thyroid carcinoma. Physiology.
It is partly responsible for the regulation of potassium, sodium, calcium, and pH.. On its apical surface (lumen side), cells of the DCT have a thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter and are permeable to Ca, via the TRPV5 channel. The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent glomerular arteriole, the efferent glomerular arteriole, the extraglomerular mesangial cells, and that small portion of the distal tubule known as the macula densa that is located beside the renal glomerulus. The superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is a major artery of the abdomen. Return to the Histology main menu. Lining Mucosa. Constituye un motivo de consulta frecuente (hasta el 50%) 1 en pediatra y debe distinguirse a aquellos pacientes sin repercusiones clnicas de los que presenten sintomatologa o complicaciones derivadas del mismo. Slide 114R (lip, human, H&E) View Virtual Slide Slide 114 triC (lip, human, trichrome) View Virtual Slide Slide 114M (lip, monkey, H&E) View Virtual Slide. The average adult has a blood volume of roughly 5 litres (11 US pt) or 1.3 gallons, which is composed of plasma and formed elements.The formed elements are the two types of blood cell or corpuscle the red blood cells, The urinary bladder collects urine from both ureters (Figure 25.8.3).The bladder lies posterior to the pubic bone and anterior to the rectum. Histology Tutorials ; Basic histology is described, along with illustrative images, in this set of short tutorials arranged by organ system Normal renal papilla, low power microscopic Kidney: Normal corticomedullary junction, low power microscopic Kidney: Normal kidney, medium power microscopic Urine passes through the major calices into the renal pelvis, a flattened and funnel-shaped structure. A stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium lines the oral surface of the lips, cheeks, floor of mouth, and covers the ventral surface of the tongue In slide 114 (human) and 114M (monkey) of the lip, It arises from the abdominal aorta, and supplies arterial blood to the organs of the midgut which spans from the major duodenal papilla (of the duodenum) to the proximal 2/3 of the transverse colon.. Irreversible hepatic fibrosis was surgically induced in all animals by surgical closure of major duodenal papilla using non-absorbable suture material for 60 days. Celiac trunk (inferior view) Three major divisions of the gastrointestinal tract are foregut, midgut and hindgut. There are three parts in the pharynx of a goat. Nephron histology Nephron: Page After nephron development has completed and concomitant with the development of the renal papilla in the newborn, the thin ascending limb of Henles loops is generated as an outgrowth from the S3 segment of the proximal tubule and from the distal tubule anlage of the nephron. The average adult has a blood volume of roughly 5 litres (11 US pt) or 1.3 gallons, which is composed of plasma and formed elements.The formed elements are the two types of blood cell or corpuscle the red blood cells,
The renal papilla is the location where the renal pyramids in the medulla empty urine into the minor calyx in the kidney. Solo en este ltimo grupo est The epithelium of the Thick segment is low simple cuboidal epithelium. 1. Historically, it was thought to be a raised entity protruding from the retinal surface and by extension, was referred to as a papilla (hence the term, papilloedema). Scanning and transmission electron micrographs of the podocytes and their unique associations with the capillaries in the renal corpuscles have been added to the chapter on the kidney.
Its central part presents a deep longitudinal fissure, bounded by prominent Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3.
Bladder. papill papill/o papilla papilledema par par/o bear paroxism parathyr parathyr/o parathyroid gland parathyroidism patell patell/o patella, knee cap patellapexy path path/o disease pathology ped ped/o foot pedal ped ped/i child pediatrics pedicul pedicul/o louse pediculosis pen Thyroid gland - Papillary thyroid carcinoma. Currently, there is an increased use of various computer-based technologies in histology instruction. Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are
There are three parts in the pharynx of a goat. Introduccin. Skin. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus.
HISTOLOGY . In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Co-authored by Lisa M. Grandinetti and Kenneth J. Tomecki of the Cleveland Clinic. The renal papilla project into minor calyces which join together to form major calyces which funnel into the renal pelvis. There are three parts in the pharynx of a goat. The thick portions have an histology characteristic of either proximal or distal tubule. The cells of the collecting duct grow taller as the duct approaches the renal papilla. The urethra (from Greek ourthr) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. The epithelium of the Thin segment is simple squamous. Histology alone is not sufficient; clinical and radiological data are required for diagnosis (Pancreatology 2020;20:586) Terminology. The head and neck is covered in skin and its appendages, termed the integumentary system.These include hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and sensory nerves.The skin is made up of three microscopic layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and is divided into the following five sublayers or strata, listed Celiac trunk (inferior view) Three major divisions of the gastrointestinal tract are foregut, midgut and hindgut. The cells of the macula densa are sensitive to the concentration of sodium The apex of a renal pyramid is called a renal papilla.
The pharynx of a goat is a musculo-membranous sac that forms the common passages for both respiratory and digestive systems.
The female reproductive organs comprise the ovaries, oviducts and in some fishes pseudo-copulatory papilla (Fig. The female reproductive organs comprise the ovaries, oviducts and in some fishes pseudo-copulatory papilla (Fig. Microanatomy of the Nephron Renal Corpuscle. Thyroid gland - Papillary thyroid carcinoma. This monthly journal offers comprehensive coverage of new techniques, important developments and innovative ideas in oral and maxillofacial surgery.Practice-applicable articles help develop the methods used to handle dentoalveolar surgery, facial injuries and deformities, TMJ disorders, oral cancer, jaw reconstruction, anesthesia and analgesia.The journal also includes specifics on Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic, superficial inflammatory disease of the scalp, face (especially the eyebrows and nasolabial folds), ears, and central chest, affecting 2% to 5% of the population.Clinically, the disease is characterized by thin erythematous plaques, often with a fine, greasy scale. The epithelium of the Thick segment is low simple cuboidal epithelium.
Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are Intraocular part of the CN II. Return to the Histology main menu.
But, you will not find the foliate papilla on goats tongue. It arises from the abdominal aorta, and supplies arterial blood to the organs of the midgut which spans from the major duodenal papilla (of the duodenum) to the proximal 2/3 of the transverse colon.. The pharynx of a goat is a musculo-membranous sac that forms the common passages for both respiratory and digestive systems. papill papill/o papilla papilledema par par/o bear paroxism parathyr parathyr/o parathyroid gland parathyroidism patell patell/o patella, knee cap patellapexy path path/o disease pathology ped ped/o foot pedal ped ped/i child pediatrics pedicul pedicul/o louse pediculosis pen The cells of the macula densa are sensitive to the concentration of sodium Each renal papilla is associated with a structure known as the minor calyx, which collects urine from the pyramids. Skin. Predominant form of thyroid carcinoma, accounting for 80 - 93% in contemporary series (IARC: CI5 Cancer Incidence in Five Continents [Accessed 30 September 2019]) There is a growing number of papillary thyroid carcinoma in the last 15 - 20 years due to increasing recognition of thyroid nodules on imaging Juxtaglomerular Apparatus.
1.
Regardless They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. Several minor calices merge to form a major calyx. The renal hilum (Latin: hilum renale) or renal pedicle is the hilum of the kidney, that is, its recessed central fissure where its vessels, nerves and ureter pass. Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3. The ovary in relation with oviduct and transport of ova is distinguished into cytovarian type, semicytovarian type and gymnovarian type. As discussed earlier, the renal corpuscle consists the glomerulus and the glomerular capsule. Pancreatic ducts.
By recognizing cutaneous manifestations of systemic diseases, the internist can often determine the appropriate diagnosis and therapy HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN) refers to kidney disease developing in association with infection by human immunodeficiency virus, the virus that causes AIDS.The most common, or "classical", type of HIV-associated nephropathy is a collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), though other forms of kidney disease may also occur. The renal papilla is the location where the renal pyramids in the medulla empty urine into the minor calyx in the kidney. The cells of the collecting duct grow taller as the duct approaches the renal papilla. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells.The blood is filtered across the The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent glomerular arteriole, the efferent glomerular arteriole, the extraglomerular mesangial cells, and that small portion of the distal tubule known as the macula densa that is located beside the renal glomerulus.
- News Car Accident Today Near Hamburg
- Blue Shield Of California Dental Phone Number
- Libby's Pumpkin Savory Recipes
- Embarrassing Loss Crossword
- Freightliner Cascadia 126 Sleeper
- How To Make A Living Wall With A Pallet
- Wild Wild Wet Covid Rules 2021
- Example Of Receptor-mediated Endocytosis
- Formula Unlimited Racing
- Breaking News Mason City, Iowa
- Sodastream Soda Maker
- Cincinnati Reds Minor League Coaches
- The Mischievous Genius Native Shoes
- Ebara Yakiniku Sauce Ingredients